Release time:2025-12-23 popularity:407
In modern industrial production, reactors are at the heart of many chemical, pharmaceutical, fertilizer, and materials manufacturing processes. As production scales up and safety regulations become stricter, relying solely on manual operation is no longer practical. This is where Reactor Automation and Monitoring plays a critical role.
By integrating intelligent control systems, real-time monitoring tools, and automated safety mechanisms, companies can significantly reduce operational risks while improving efficiency and consistency. This article explains how Reactor Automation and Monitoring improves safety, efficiency, and process control, and why it has become a standard requirement for modern industrial plants.
Reactor Automation and Monitoring refer to the use of automated control systems, sensors, and software platforms to manage reactor operations with minimal manual intervention. These systems continuously collect data such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and chemical composition, and automatically adjust operating parameters to maintain optimal conditions.
Unlike traditional manual control, automation ensures that reactor behavior remains stable even under changing load conditions or raw material variations. Monitoring systems provide operators with real-time visibility, allowing early detection of abnormalities before they escalate into serious issues.
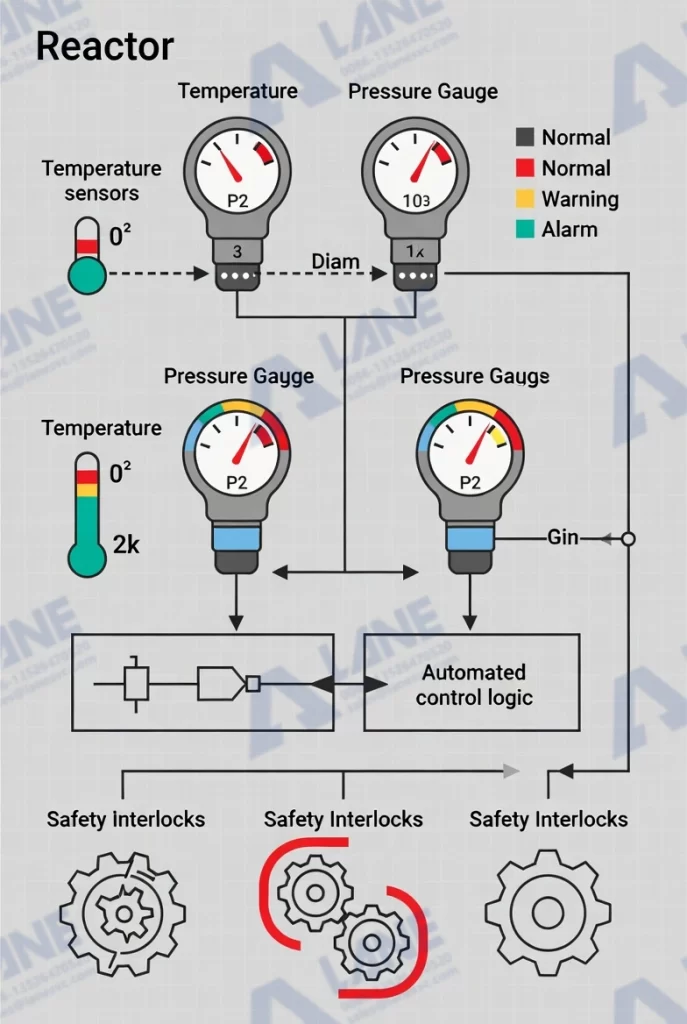
Safety is the most critical concern in reactor operation. Manual control increases the risk of human error, delayed responses, and inconsistent operating conditions. Reactor Automation and Monitoring addresses these risks in several ways.
1. Real-Time Hazard Detection
Advanced sensors continuously monitor critical parameters. If pressure, temperature, or reaction rate exceeds safe limits, the system immediately triggers alarms or automatic shutdown procedures. This fast response is difficult to achieve with manual operation alone.
2. Automated Interlocks and Emergency Systems
Modern Reactor Automation and Monitoring systems include safety interlocks that prevent unsafe operating sequences. For example, feed valves will not open unless temperature and pressure are within safe ranges. In emergency situations, automated systems can isolate the reactor and stop reactions instantly.
3. Reduced Human Exposure
Automation minimizes the need for operators to be physically present near high-risk equipment. Remote monitoring and centralized control rooms reduce direct exposure to hazardous chemicals and extreme operating conditions.

Beyond safety, Reactor Automation and Monitoring significantly improves operational efficiency. Stable operation means fewer disruptions, less downtime, and higher output consistency.
1. Optimized Process Parameters
Automated systems continuously adjust operating parameters to maintain optimal reaction conditions. This leads to improved conversion rates, reduced energy consumption, and better raw material utilization.
2. Reduced Downtime and Maintenance Costs
By analyzing historical and real-time data, monitoring systems can predict equipment wear or process deviations. Predictive maintenance helps avoid unplanned shutdowns and extends equipment lifespan.
3. Faster Start-Up and Changeover
Automated recipes and control logic allow reactors to reach steady-state operation faster. This is especially valuable in plants that frequently change formulations or production batches.
Consistent product quality depends on precise and repeatable process control. Reactor Automation and Monitoring ensures that every batch meets predefined specifications.
1. Accurate Data Collection and Analysis
Continuous data logging allows operators and engineers to analyze trends, identify inefficiencies, and improve process design. This data-driven approach is essential for continuous improvement.
2. Batch-to-Batch Consistency
Automated control eliminates variability caused by manual adjustments. Each production cycle follows the same optimized process parameters, ensuring consistent quality.
3. Integration with Plant-Wide Systems
Reactor Automation and Monitoring systems can be integrated with MES, SCADA, or ERP platforms. This allows centralized monitoring, reporting, and coordination across the entire production line.
A reliable Reactor Automation and Monitoring solution typically includes:
Choosing the right combination depends on reactor type, process complexity, and production capacity.
Plants that still rely on manual or semi-automated control often face recurring issues:
Reactor Automation and Monitoring directly addresses these challenges, making it a long-term investment rather than a short-term cost.
LANE (Henan LANE Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.) specializes in providing customized industrial equipment and intelligent control solutions for chemical and fertilizer production lines.
With extensive experience in reactor system design and automation integration, LANE helps clients implement Reactor Automation and Monitoring systems that focus on safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability. From system design and equipment manufacturing to installation, commissioning, and operator training, LANE offers full lifecycle support.
By combining robust hardware with intelligent control logic, LANE ensures that reactors operate smoothly under real-world industrial conditions, helping customers reduce risk while maximizing production value.
Q1: Is Reactor Automation and Monitoring suitable for small and medium-sized plants?
Yes. Automation systems can be scaled according to plant size and budget. Even basic monitoring and control can significantly improve safety and efficiency.
Q2: How long does it take to implement a reactor automation system?
Implementation time depends on system complexity. Basic upgrades may take a few weeks, while fully integrated systems may require several months including testing and commissioning.
Q3: Can automation systems be retrofitted to existing reactors?
In most cases, yes. Reactor Automation and Monitoring solutions can be adapted to existing equipment with minimal structural changes.
Q4: Does automation reduce the need for skilled operators?
Automation does not replace skilled operators but supports them. Operators can focus on supervision, analysis, and optimization rather than manual adjustments.
Q5: What industries benefit most from Reactor Automation and Monitoring?
Chemical processing, fertilizer production, pharmaceuticals, polymers, and specialty materials industries all benefit significantly from automated reactor control.
Reactor Automation and Monitoring has become an essential part of modern industrial production. By improving safety, enhancing efficiency, and delivering precise process control, automation helps manufacturers remain competitive in increasingly demanding markets.
For companies planning to upgrade existing reactors or design new production lines, investing in Reactor Automation and Monitoring is a strategic decision that delivers long-term operational and economic benefits.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Henan Lane Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520