Release time:2025-12-02 popularity:407
In modern fertilizer and chemical plants, the reactor is the heart of the production process. Whether a plant is producing phosphates, compound fertilizers, or specialty chemicals, the stability and efficiency of the reactor determine product quality, operational safety, and long-term reliability. This is why professional reactor installation and commissioning has become a critical engineering task rather than a simple equipment setup procedure. When done properly, it lays the foundation for stable reactions, energy savings, reduced maintenance, and continuous high-efficiency production.
Before diving into installation and commissioning, it is important to understand why reactors require such careful engineering. Modern production lines often operate under high temperature, high pressure, and corrosive environments. Reactors—whether stainless-steel, alloy, or glass-lined—must accommodate mechanical stress, thermal cycling, and precise mixing requirements. Any error during installation may lead to leaks, unbalanced reactions, or premature equipment failure. In fertilizer plants where reactions can be highly exothermic, proper setup is not only an engineering requirement but also a strong safety guarantee.
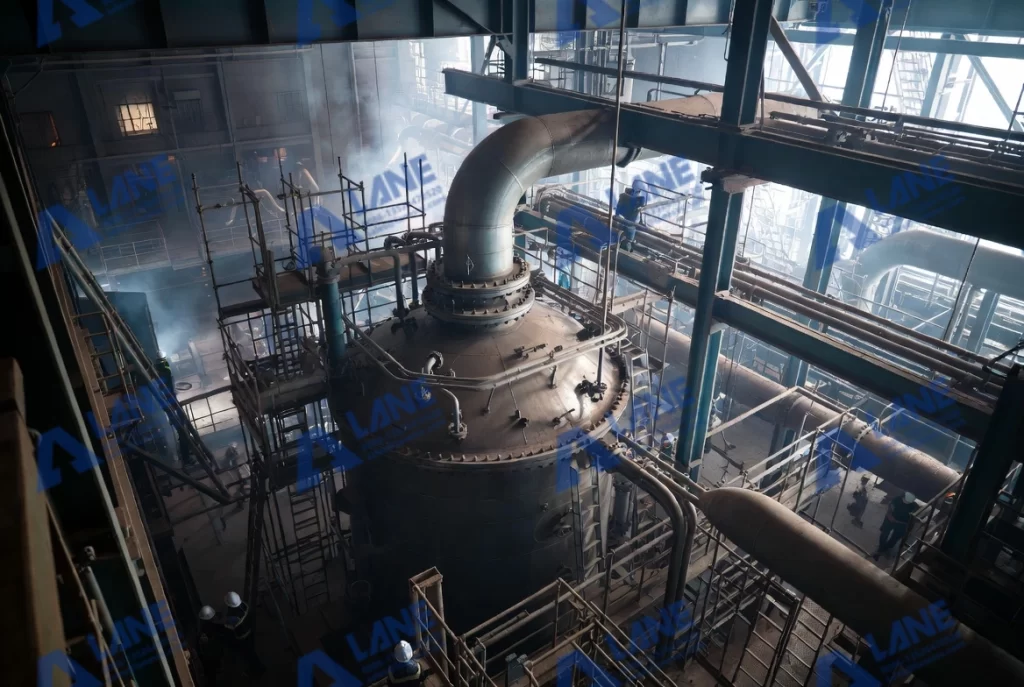

Successful reactor installation and commissioning begins long before the equipment arrives on site. Engineers usually start with a design review to confirm that layout drawings, foundation dimensions, and pipeline routes match actual site conditions. This phase is essential because even minor deviations in anchor bolt locations or pipeline orientation can cause misalignment later.
Preparing the installation area is equally important. A stable foundation, sufficient working space, accessibility for cranes, and clear maintenance zones ensure a smooth installation process. Proper documentation—often overlooked by inexperienced teams—also determines whether reactor installation and commissioning can proceed safely. Certificates, P&ID diagrams, control system drawings, and material test reports must all be verified before the project continues.
Reactor installation requires precision and coordination. When the equipment is lifted, engineers must monitor rigging angles, lifting points, and rotation to avoid impact damage. Once placed on the foundation, the reactor is aligned using laser or dial indicators to achieve the required tolerance. Proper alignment is crucial because even small deviations may cause excessive vibration or seal failure during operation.
The next stage involves connecting the reactor to utilities and process pipelines. Steam, cooling water, compressed air, and material feeds must be installed according to the engineering design. Instrumentation—including temperature sensors, pressure transmitters, flow meters, and safety interlocks—must be integrated with the plant’s PLC system. A clean and accurate installation ensures that the later commissioning phase proceeds smoothly.
Commissioning is the true test of whether reactor installation and commissioning has been done correctly. The process generally starts with cold commissioning. Engineers run the reactor without heating or material loading to verify electrical connections, motor rotation, lubrication, cooling pathways, and control system communication. Cold tests help detect early issues such as abnormal vibration or misconfigured sensors.
Once cold commissioning is complete, hot commissioning begins. This stage simulates real reaction conditions and further confirms the quality of reactor installation and commissioning. The reactor is gradually heated to operating temperature while engineers monitor pressure stability, heat transfer performance, foam formation, and reaction uniformity. Any anomaly—temperature fluctuations, response delays, or mixing inconsistency—must be addressed before entering full production. Hot commissioning is also the moment when safety systems are validated, including interlocks, emergency shutdowns, and relief devices.
Temperature stability during heating
Pressure response and relief system accuracy
Mixer torque and vibration performance
Instrumentation calibration
System startup and shutdown sequence validation
These checks ensure that reactor installation and commissioning meets both engineering and safety standards.
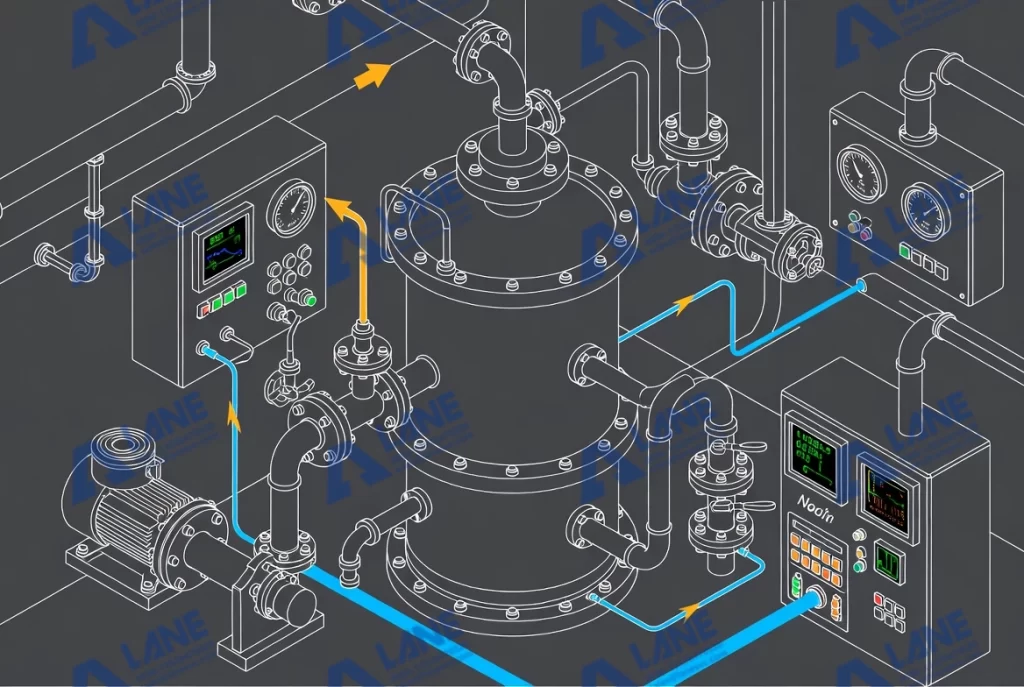
A reactor is a long-term investment that often runs continuously for years. Its stability depends more on the quality of installation and commissioning than on the equipment itself. A poorly installed reactor may suffer from seal leaks, heat transfer inefficiencies, uneven mixing, or unexpected shutdowns. In contrast, professional installation reduces operational risk, increases production capacity, extends equipment lifespan, and ensures compliance with industry standards.
1. What is included in reactor installation and commissioning?
It includes positioning the equipment, aligning critical components, connecting utilities, testing instrumentation, and performing cold and hot commissioning to verify safe and stable operation.
2. Why is commissioning necessary for modern fertilizer and chemical plants?
Commissioning ensures that the reactor can operate safely under real reaction conditions, making it an essential step for plants handling high-temperature or corrosive processes.
3. How long does the reactor installation and commissioning process take?
Depending on the plant scale and reactor size, it usually requires one to four weeks, including mechanical installation, cold testing, and hot reaction validation.
4. What problems can poor installation cause?
Issues may include leaks, unstable mixing, excessive vibration, poor temperature control, and reduced reaction efficiency—problems that can be avoided through professional execution.
Reactor installation and commissioning is far more than a mechanical task—it is an engineering discipline that directly influences a plant’s long-term success. Every modern fertilizer or chemical manufacturer depends on stable reaction performance, and that stability begins with how the reactor is placed, aligned, tested, and validated. Plants that invest in professional installation and commissioning ultimately achieve better efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and safer operations.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Henan Lane Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520